본문
| Department | Pharmacology |
|---|---|
| Major Field of Research | Cardiovascular Pharmacology |
| kookhyun@jnu.ac.kr | |
| Homepage |
Research interests
The Kook Hyun Professor's Laboratory is performing research on the following topics using various cardiovascular disease animal models and metabolic disease animal models.
1. Role of Circular RNA in the Differentiation of Myocardial and Fibroblast
- CircRNA is a single helix with a circular structure, and more than 10,000 are known to humans at present, but it is very few that have been found to have function or mechanism of action. In particular, some of the circular RNAs are known to produce proteins and their functions vary widely.
- Using analysis of RNA sequencing and GEO data, we identified novel circular RNAs in cardiomyocardial and fibroblast cells related to cardiac hypertrophy/cardiodeficiency and are conducting functional studies.
2. Function of pCAF in Cardiac Fibrosis and Vascular Calcification
- Previous we reported that the acetylation of HDAC2 is mediated by pCAF in cardiac hypertrophy (Circ Res, 2014). We generated pCAF KO mice using CRISPR/CAS9 method to elucidate the function and new acetylation target of pCAF in cardiac and vascular calcification models.studies.
3. Identification of RFP functions and roles in fat metabolism;
- Due to the development of westernized eating habits and various means of transportation, the obesity population of modern people is continuously increasing due to the decrease in physical activity, and it is a major cause of increasing mortality due to various metabolic diseases. In particular, metabolic symptom root such as hypertension, obesity, hypertriglyceridemia and diabetes acts as a risk factor to increase mortality and prevalence by promoting cardiovascular disease as well as cancer.
- Recently, we observed the decrease in weight and body fat accumulation in high-fat RFP KO mice. Therefore, we are studying to identify RFP function in the process of adipose differentiation.
4. Molecular mechanism of vascular remodeling
- Vascular remodeling is caused in cardiovascular disease such as aging, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, overweight, diabetes, smoking, etc., which causes endothelial cell damage, vascular smooth muscle proliferation and vascular calcification, which reduces the elasticity of blood vessels.
- This study is to provide basic and clinical knowledge for the treatment of vascular diseases and related complications by understanding and revealing the mechanism of vascular remodeling due to various causes.
- We are studying with our collarbolators to identify the mechanisms of vascular remodeling and develop novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease.
5. Molecular mechanisms of Regulation in skeletal muscle differentiation
- Skeletal muscle, when accompanied by aging or metabolic disease, is significantly reduced in regeneration ability, so it is necessary to develop selective treatments that induce muscle regeneration more actively in preparation for muscle mass reduction.
- We are investigating the mechanism of epigenetic regulation such as methylation and acetylation and non-coding RNA including miRNA, circular RNA and lncRNA, in the skeletal muscle differentiation processes.
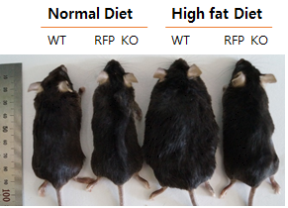
1. 고지방식이 먹인 wild type 쥐와 RFP KO쥐 비교 사진
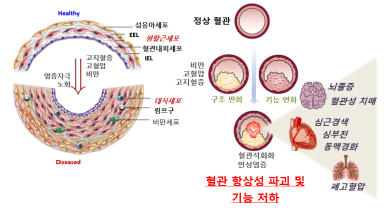
혈관 리모델링 연구 도해
Publication
- Choe N, Shin S, Joung H, Ryu J, Kim YK, Ahn Y, Kook H*, and Kwon DH*. (2020) The microRNA miR-134-5p induces calcium deposition by inhibiting histone deacetylase 5 in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Mol Med. 24(18):10542-50.
- * co-corresponding authors
- Choe N, Kwon DH, Ryu J, Shin S, Cho HJ, Joung H, Eom GH, Ahn Y, Park WJ, Nam KI, Kim YK*, Kook H*. (2020) miR-27a-3p Targets ATF3 to Reduce Calcium Deposition in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 22:627-639. * co-corresponding authors
- Lim YH, Ryu J, Kook H*, Kim YK*. (2020) Identification of Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in Differentiation and Survival of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 22:209-221.
- * co-corresponding authors
- Ryu J, Ahn Y, Kook H*, Kim YK*. (2020) The roles of non-coding RNAs in vascular calcification and opportunities as therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Ther. 8:107675. * co-corresponding authors
- Kwon DH, Ryu J, Kim YK*, Kook H* (2020) Roles of Histone Acetylation Modifiers and Other Epigenetic Regulators in Vascular Calcification. Int J Mol Sci. 21(9):3246. * co-corresponding authors
- Kang JY, Kim JY, Kim KB, Park JW, Cho H, Hahm JY, Chae YC, Kim D, Kook H, Rhee S, Ha NC, Seo SB. (2018) KDM2B is a histone H3K79 demethylase and induces transcriptional repression via sirtuin-1-mediated chromatin silencing. FASEB J. 32(10):5737-5750. * co-corresponding authors
- Gorski PA, Jang SP, Jeong D, Lee A, Lee P, Oh JG, Chepurko V, Yang DK, Kwak TH, Eom SH, Park ZY, Yoo YJ, Kim DH, Kook H, Sunagawa Y, Morimoto T, Hasegawa K, Sadoshima J, Vangheluwe P, Hajjar RJ, Park WJ, Kho C. (2019) Role of SIRT1 in Modulating Acetylation of the Sarco-Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in Heart Failure. Circ Res. 2019 124(9):e63-e80.
- Ryu J, Kwon DH, Choe N, Shin S, Jeong G, Lim YH, Kim J, Park WJ, Kook H*, Kim YK*. (2020) Characterization of Circular RNAs in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells with Vascular Calcification. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.19:31-41. * co-corresponding authors
- Joung H, Kwon S, Kim KH, Lee YG, Shin S, Kwon DH, Lee YU, Kook T, Choe N, Kim JC, Kim YK, Eom GH*, Kook H*. (2018) Sumoylation of histone deacetylase 1 regulates MyoD signaling during myogenesis. Exp Mol Med. 50(1):e427. * co-corresponding authors
- Yoon S, Kook T, Min HK, Kwon DH, Cho YK, Kim M, Shin S, Joung H, Jeong SH, Lee S, Kang G, Park Y, Kim YS, Ahn Y, McMullen JR, Gergs U, Neumann J, Kim KK, Kim J, Nam KI, Kim YK, Kook H*, Eom GH*. (2018) PP2A negatively regulates the hypertrophic response by dephosphorylating HDAC2 S394 in the heart. Exp Mol Med. 50(7):1-14. * co-corresponding authors
- Yoon S, Kim M, Min HK, Lee YU, Kwon DH, Lee M, Lee S, Kook T, Joung H, Nam KI, Ahn Y, Kim YK, Kim J, Park WJ, McMullen JR, Eom GH*, Kook H*. (2019) Inhibition of heat shock protein 70 blocks the development of cardiac hypertrophy by modulating the phosphorylation of histone deacetylase 2. Cardiovasc Res. 115(13):1850-1860. * co-corresponding authors
- Kwon DH, Eom GH, Ko JH, Shin S, Joung H, Choe N, Nam YS, Min HK, Kook T, Yoon S, Kang W, Kim YS, Kim HS, Choi H, Koh JT, Kim N, Ahn Y, Cho HJ, Lee IK, Park DH, Suk K, Seo SB, Wissing ER, Mendrysa SM, Nam KI, Kook H. (2016) MDM2 E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of HDAC1 in vascular calcification. Nat Commun. 27:10492.